Glossary of Tesla Terms Extended
Thomas Valone, The Creator One
Original: Excerpt adapted from "Project Insight: A Study of Tesla's Advanced Concepts",
H. W. Jones
Author: H. W. Jones; Thomas Valone. Extenden by: The Creator One
Excerpt adapted from "Project Insight: A Study of Tesla's Advanced Concepts," H. W. Jones,
Proceedings of the Tesla Centennial Symposium, 1984.
By clicking on the glossary word*,
more explanation will appear.
Advanced Concepts:
Those ideas which Tesla was known to have conceived and
developed to some extent, but did not pursue to fruition because of lack of funding and
laboratory facilities. The more dramatic of these concepts were: free energy, wireless
transmission of energy, employment of scalar technology, non-Hertzian waves, the Tesla
shield, the Tesla ray.
Cold Electricity*:
Tesla discovered a new type of energy - the cold electricity - which can
be generated by using electromagnetic pulses (EMP).
Cold Electricity is a very unusual type of energy flow generated by longitudinal electric wave.
For this type of electricity, resistance has no effect, and where this energy changes
into another type of energy (light, magnetic field in motor, loading battery...)
the equipment will be even cooler, not hot).
Unfortunatelly, we don't know a way to separate conventional current form cold electricity.
Ball Lightning:
A form of lightning in which a slow-moving, extremely high temperature
sphere forms. Only rarely seen in nature, but producible by artificial means. Currently being
used in the study of harnessing fusion energy for commercial use.
DeBroglie Wave:
The quantum mechanics wave associated with a particle of matter
which can theoretically give rise to intra-atomic interference effects. In his speech accepting
the Nobel Prize, DeBroglie emphasized that these waves are real and must not be regarded
simply as mathematical oddities or conveniences.
Electric explosion*:
Phenomena manifest themselves when the criteria
for voltage or potential difference is instantly disrupted, as with a short circuit.
Phenomena of enormous magnitude manifest themselves when the criteria
for voltage or potential difference is instantly disrupted, as with a short circuit.
The effect is analogous with the open circuit of inductive current. Because the forcing
voltage is instantly withdrawn the field explodes against the bounding conductors with
a velocity that may exceed light. Because the current is directly related to the velocity
of field it jumps to infinity in its attempt to produce finite voltage across zero resistance.
If considerable energy had resided in the dielectric force field, again let us say several
KWH the resulting explosion has almost inconceivable violence and can vaporize a conductor
of substantial thickness instantly. Dielectric discharges of great speed and energy represent
one of the most unpleasant experiences the electrical engineer encounters
in practice.
Electrical collapse*:
Phenomena manifest themselves when
the current path is interrupted.
The field is attempting to maintain current by producing whatever EMF required.
.
Very interesting (and dangerous) phenomena manifest themselves when
the current path is interrupted, thereby causing infinite resistance to appear.
In this case resistance is best represented by its inverse, conductance.
The conductance is then zero. Because the current vanished instantly the field
collapses at a velocity approaching that of light. As EMF is directly related to
velocity of flux, i tends towards infinity. Very powerful effects are produced
because the field is attempting to maintain current by producing whatever EMF required.
If a considerable amount of energy exists, say several kilowatt hours*
(250 KWH for lightning stroke), the ensuing discharge can produce most profound effects
and can completely destroy inadequately protected apparatus.
Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP):
A sharp pulse of energy and electromagnetic radiation
occurring when an explosion occurs in an unsymmetrical envrionment. Tesla theorized that an
EMP would result when two longitudinal scalar electrostatic potential wave patterns met and
coupled into a flash of vector electromagnetic energy.
Electromagnetic Theory (EMT)*:
Conventional electrical theory currently taught in our
educational system, mainly giving credit only to Hertz, Maxwell, and Faraday. Tesla's work
challenged the adequacy of existing EM theory, as do many physicists today. EM theory is
only good for "far field" EM waves, as only electrical engineering EM textbooks (e.g. Magid)
will admit.
The recommended physical perspective, is to ask whether we are within the "near
field," i.e., within the first couple of wavelengths. In this region, a capacitively-created EM
wave will still retain mainly electrical characteristics and can be stopped by a Faraday cage.
However, a inductively-created EM wave will still retain mainly magnetic characteristics and
go right through even the most expensive Faraday cage (made with Mu Metal) such as the
quarter-million dollar one at Wright-Patterson AFB. Especially when dealing with extremely
low frequency (ELF), most staunch EM theorists are stymied because we are always within
the near field with ELF waves.
The new EMT (Steinmetz 1912, Dollard 1970?) describes the electric energy as the sum of
two different energy forms - dielectrical an electrical, and describes the interaction between
these two forms.
Electromagnetic Wave*:
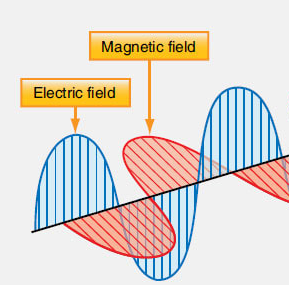 A Hertzian wave. A wave that oscillates
transversely rather than longitudinally, having electric (E) field and magnetic (B) field
effects (each may be detected). If two sine waves are pictured, perpendicular
to each other, one on the x-y plane (vertical) and the other on the x-z
plane (horizontal), both traveling in the x-direction, the E-field will be
designated by the x-y plane wave (if it is polarized light) and the B-
field will be the x-z plane wave. Polaroid® sunglasses work because
they only let the E-field light through if it is in the x-y plane, whereas any reflected glare will
have the E-field oscillating in the x-z plane (which is horizontal). Non-Hertzian waves are not
transverse and often occur because near field, distorted waves are created in the experiment.
A Hertzian wave. A wave that oscillates
transversely rather than longitudinally, having electric (E) field and magnetic (B) field
effects (each may be detected). If two sine waves are pictured, perpendicular
to each other, one on the x-y plane (vertical) and the other on the x-z
plane (horizontal), both traveling in the x-direction, the E-field will be
designated by the x-y plane wave (if it is polarized light) and the B-
field will be the x-z plane wave. Polaroid® sunglasses work because
they only let the E-field light through if it is in the x-y plane, whereas any reflected glare will
have the E-field oscillating in the x-z plane (which is horizontal). Non-Hertzian waves are not
transverse and often occur because near field, distorted waves are created in the experiment.

The waves are in the most pictures bad shown, because the electic and the magnetic fields are
in continuous changing energy with each other, therefore, they are shifted in 90 degree to each
other. Imagine it as a rotating entity, where the rotating speed can be measured with its
frequency.
(Click on the picture beside.) The energy quantum (foton) is always a multiples of
"Planck's constant" (denoted as ℎ, approximately equal to 6.626×10-34 J·s).
Energy*:
Energy is the ability to do work or cause change.
(Classical physics) The capacity to do work, which is the result of a force moving a mass through a
distance. Measured in "joules" it is the timeless version of power times time, such as kilowatt-
hours (kWh). For Tesla science: see zero-point energy.
Ether:
Simply stated, it is the same as the physical vacuum. This differs
from the common understanding of empty space, since theorists regard the ether (and the
physical vacuum) as having substance (and particles in negative energy states). With the
Silvertooth experiments, now showing a preference of direction for the old Michelson-Morley
type of experiment, the ether is coming back into vogue. Very compatible with Eastern
mysticism.
Extremely low frequency (ELF)*:
Electromagnetic radiation with frequencies from 3 to 30 Hz,
and corresponding wavelengths of 100,000 to 10,000 kilometers, respectively.
It may be used in the medicine for different purposes.
Free Energy*:
Energy which is free. Often confused with perpetual motion, free energy
has three aspects;
- no cost for input
- plentiful and inexhaustible
- one-time capital expenditure.
Renewable energy is free energy, Zero point energy (ZPE) is also free and
equated with the ether. A prophetic endorsement for free energy comes from Tesla's comment
that "it is a mere question of time when men will succeed in attaching their machinery to the
very wheelwork of nature." 1 He implies, what was discovered years later, that in open
systems, it appears that energy is not conserved (e.g. ZPE vacuum fluctuations).
However, in
closed systems, we know that the second law of thermodynamics and energy conservation
laws apply. Compare with the physics definition G = H - TS where G is "Gibb's free energy,"
H is enthalpy, T is absolute temperature, and S is entropy. In words, free energy is the internal
energy of a system minus the product of its temperature and its entropy.
Frequency (Teslian):
Frequency refers to the repetition of pulses per second.
Gravity*:
 The phenomenon characterized by the physical
attraction of any two material
bodies, defined as the product of the masses divided by the
square of the distance between
them. The fact that gravity is
always attractive and never repulsive (contradics Newton low,
because is has no counterforce) is a curiosity that
physicists have always wondered about. The fact that
gravity has to travel many times faster than light speed to
prevent aberrations has caused a lot of commotion.
The phenomenon characterized by the physical
attraction of any two material
bodies, defined as the product of the masses divided by the
square of the distance between
them. The fact that gravity is
always attractive and never repulsive (contradics Newton low,
because is has no counterforce) is a curiosity that
physicists have always wondered about. The fact that
gravity has to travel many times faster than light speed to
prevent aberrations has caused a lot of commotion.
Tesla talked about controlling gravity many times.
There are many accepted modalities for creating artificial gravity and
antigravity with high energy electromagnetism.
Longitudinal Wave*:
A "pressure" type of wave, similar to sound, in which the vibrations are along
the direction of travel, a sequence of compressions and rarefactions. Longitudinal waves are
nonHertzian. Longitudinal scalar waves can penetrate a standard Faraday Cage;
transverse vector waves (EM, "Hertzian") cannot.
Longitudinal wave has another speed in the medium than the transvers wave.
Best analogy is the wave in water.
Radiant Energy*:
Term used by Tesla in his two 1901 patents, and by Dr. Moray
to describe the source of energy from the ether.
Also John Bedini uses these words for his experiments, and we call this
today as 'Zero-Point Energy'. In this collecton of papers and books we prefer
to use the term 'Radiant Energy' in restricted sense.
We use it only for energy related to 'Radiant Wave'. Radiant energy engineering means
here the collection of energy flow generated by radiant wave.
Radiant Wave*:
Radiant wave arises by electrical collapse (the current path is interrupted).
It is a longitudinal wave and orthogonal to the wire where the current has flown.
The theory describes the radiant wave as a disturbance in the ether. If the disturbance is
big enought, it is possible to get out more energy through the ether then needed to maintain this
disturbance.
Reactance*:
'Massless' radiant energy, or "cosmic radiation", is dynamic energy stored in transit
in space, by the vibrations of the ether. Define space as a volume, which is never empty,
but contains ether, and omnidirectionally interpenetrating energy of many frequencies.
The energy level of this energy is determined by its frequency.
This type of energy is the ZPR.
Measure of the opposition that a circuit or a part of a circuit
presents to electric current insofar as the current is varying or alternating.
Steady electric currents flowing along conductors in one direction undergo
opposition called electrical resistance, but no reactance.
Reactance is present in addition to resistance when conductors carry
alternating current.(Classic definition, meassured in Ohm.)
Resonance (Teslian):
Resonance refers to conditions in which aether flows with little or no resistance
through systems, whether proximal or widely separated.
Scalar Field:
In physics, each point in space for a particulas potential is assigned a
magnitude but no direction. The scalar potention is just the Coulomb potential
due to a charged density p(x,t). While EM waves travel at light speed,
the "scalar Potential 'propagates' instantaneously everywhere in space".
Scalar Wave*:
(See Longitudinal Wave.) Also referred to as a Tesla Wave. An electrostatic scalar
potential wave which, in the absence of spinning charged mass particles, does not form
a vector electromagnetic wave, in contradictinction to present electromagnetic theory.
A changing (most oscillating) scalar potential in the space.
Because no energy or momentum transfer occures, this wave (wave: change of field) can penetrate all objects and in fact
can traverse the whole universe. Scalar waves thus may in fact, travel fasten than light speed
c, since no c-limited fields are involved.
Tesla Fireball:
(See Ball Lightning.) Interference of two scalar Fourier expansion
patterns to form a glowing, fiery ball of radiant electromagnetic
energy. A self-sustaining ball of radiant energy, exhibiting soliton behavior.
Soliton: nonlinear, self-reinforcing, localized wave packet that is strongly stable,
in that it preserves its shape while propagating freely, at constant velocity,
and recovers it even after collisions with other such localized wave packets.
Tesla Ray:
Forerunner of the laser. An electronic device demonstrated by Tesla,
and offered by him to the British Government in 1937
as a defense against the potential Luftwaffe threat. It was ridiculed and rejected.
There is a variation called the Tesla Death Ray, which was a particle beam weapon.
Transverse Wave:
A standard Hertzian vector wave which oscillates laterally,
as contrasted with a Tesla electrostatic scalar wave
which vibrates longitudinally.
Vacuum:
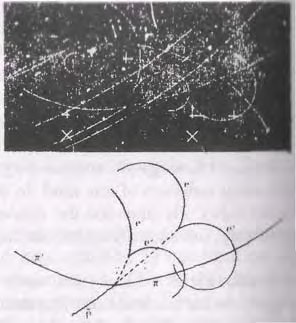 A plenum which is filled
with particles in negative energy states. Dr. Paul Dirac
became a Nobel Prize winner for predicting the
existence of the positron (antimatter electron with
positive charge) after theorizing that under high
voltage circumstances, and electron-positron pair can
emerge, like magic, from the vacuum and go off in
opposite directions, Such experiments (shown here
with cloud chamber picture) have verified the vacuum
is teaming with activity. See zero-point energy.
A plenum which is filled
with particles in negative energy states. Dr. Paul Dirac
became a Nobel Prize winner for predicting the
existence of the positron (antimatter electron with
positive charge) after theorizing that under high
voltage circumstances, and electron-positron pair can
emerge, like magic, from the vacuum and go off in
opposite directions, Such experiments (shown here
with cloud chamber picture) have verified the vacuum
is teaming with activity. See zero-point energy.
Vector:
A force or field that has magnitude and
direction, compared with scalar fields. EM waves are
vector fields and contain momentum.
Wardenclyffe:
Name of the first transmission tower in the world, erected 1901-3 in
Shoreham, NY by Tesla which rose to a height of 187 feet. The Tesla Wardenclyffe Project.
Zero-Point Energy (ZPE)*:
The energy of the vacuum that is sustained even at zero absolute
temperature and no air (complete vacuum). This is the "very wheelwork of nature" and even
implicated in the antigravity effect seen on the acceleration of distant galaxies (Science, Dec,
1998) The Casimir effect, experimentally verified, shows that virtual particles, as they emerge
from the vacuum, also exert a measurable force. It is
predicted that, since the ZPE Casimir force already exhibits perpetual wavy motion already in
nanotechnology (endless oscillations of nanostructures under tensile stress).
See Planck's equation from 1911.
Throughout space there is an energy. Is this energy static or kinetic?
If static, our hopes are in vain. If kinetic, and we know for certain it is,
then it is a mere question of time when men will succeed in attaching their machinery
to the very wheelwork of nature.
Many generation may pass, but in time our machinery will be driven
by a power obtainable at any point in the universe.
-Nikola Tesla
ZPR*:
Zero Point Radiation. There is an ultra high frequency, ubiquitous radiation,
normally in equilibrium, called Zero Point Radiation (“ZPR”), which interpenetrates the ether, and
represents electromagnetic radiation in its finest, densest form, which, in conjunction with the ether,
conserves universal perpetual motion.
ZPR has no temperature dependency.
 A Hertzian wave. A wave that oscillates
transversely rather than longitudinally, having electric (E) field and magnetic (B) field
effects (each may be detected). If two sine waves are pictured, perpendicular
to each other, one on the x-y plane (vertical) and the other on the x-z
plane (horizontal), both traveling in the x-direction, the E-field will be
designated by the x-y plane wave (if it is polarized light) and the B-
field will be the x-z plane wave. Polaroid® sunglasses work because
they only let the E-field light through if it is in the x-y plane, whereas any reflected glare will
have the E-field oscillating in the x-z plane (which is horizontal). Non-Hertzian waves are not
transverse and often occur because near field, distorted waves are created in the experiment.
A Hertzian wave. A wave that oscillates
transversely rather than longitudinally, having electric (E) field and magnetic (B) field
effects (each may be detected). If two sine waves are pictured, perpendicular
to each other, one on the x-y plane (vertical) and the other on the x-z
plane (horizontal), both traveling in the x-direction, the E-field will be
designated by the x-y plane wave (if it is polarized light) and the B-
field will be the x-z plane wave. Polaroid® sunglasses work because
they only let the E-field light through if it is in the x-y plane, whereas any reflected glare will
have the E-field oscillating in the x-z plane (which is horizontal). Non-Hertzian waves are not
transverse and often occur because near field, distorted waves are created in the experiment. The waves are in the most pictures bad shown, because the electic and the magnetic fields are
in continuous changing energy with each other, therefore, they are shifted in 90 degree to each
other. Imagine it as a rotating entity, where the rotating speed can be measured with its
frequency.
The waves are in the most pictures bad shown, because the electic and the magnetic fields are
in continuous changing energy with each other, therefore, they are shifted in 90 degree to each
other. Imagine it as a rotating entity, where the rotating speed can be measured with its
frequency. The phenomenon characterized by the physical
attraction of any two material
bodies, defined as the product of the masses divided by the
square of the distance between
them. The fact that gravity is
always attractive and never repulsive (contradics Newton low,
because is has no counterforce) is a curiosity that
physicists have always wondered about. The fact that
gravity has to travel many times faster than light speed to
prevent aberrations has caused a lot of commotion.
The phenomenon characterized by the physical
attraction of any two material
bodies, defined as the product of the masses divided by the
square of the distance between
them. The fact that gravity is
always attractive and never repulsive (contradics Newton low,
because is has no counterforce) is a curiosity that
physicists have always wondered about. The fact that
gravity has to travel many times faster than light speed to
prevent aberrations has caused a lot of commotion. Longitudinal wave has another speed in the medium than the transvers wave.
Best analogy is the wave in water.
Longitudinal wave has another speed in the medium than the transvers wave.
Best analogy is the wave in water. A plenum which is filled
with particles in negative energy states. Dr. Paul Dirac
became a Nobel Prize winner for predicting the
existence of the positron (antimatter electron with
positive charge) after theorizing that under high
voltage circumstances, and electron-positron pair can
emerge, like magic, from the vacuum and go off in
opposite directions, Such experiments (shown here
with cloud chamber picture) have verified the vacuum
is teaming with activity. See zero-point energy.
A plenum which is filled
with particles in negative energy states. Dr. Paul Dirac
became a Nobel Prize winner for predicting the
existence of the positron (antimatter electron with
positive charge) after theorizing that under high
voltage circumstances, and electron-positron pair can
emerge, like magic, from the vacuum and go off in
opposite directions, Such experiments (shown here
with cloud chamber picture) have verified the vacuum
is teaming with activity. See zero-point energy.